Electric heating tubes are widely used in both industrial and civilian applications, primarily to convert electrical energy into heat energy for heating target objects. However, when using electric heating tubes, determining the characteristics of the heating object and its temperature control conditions is crucial. This not only affects the heating efficiency but also relates to the safety and lifespan of the equipment. This article will discuss how to determine the heating conditions for electric heating tubes based on heating power and heating medium.

I. Determining the Heating Power
Heating power is one of the important parameters of electric heating tubes, determining the speed and effectiveness of heating. When identifying the heating object, it is essential to determine the appropriate heating power. The determination of heating power typically involves considering the following factors:
1. Thermal Capacity of the Heating Object: Different materials have different specific heat capacities. Materials with large thermal capacities require higher heating power. For example, water has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it requires more energy to heat compared to metals under the same conditions. Therefore, for mediums with large thermal capacities, a higher power electric heating tube should be chosen.
2. Mass of the Heating Object: The greater the mass, the higher the required heating power. For instance, heating 1 liter of water and heating 10 liters of water require different power levels. Generally, the heating power should be proportional to the mass of the heating object.
3. Heating Time Requirements: If rapid heating is required, a higher power electric heating tube should be selected. Conversely, if a longer heating time is acceptable, a lower power heating tube can be chosen to save energy.
4. Environmental Temperature and Heat Loss: In low-temperature environments or where there is significant heat loss during the heating process, a higher power electric heating tube is needed to compensate for the heat loss. In environments with poor insulation, higher heating power can ensure that the target object reaches the required temperature.
II. Determining the Heating Medium
The choice of heating medium significantly impacts the selection of electric heating tubes and the setting of temperature control conditions. The heating medium can be solid, liquid, or gas, each with different physical properties and heating requirements.
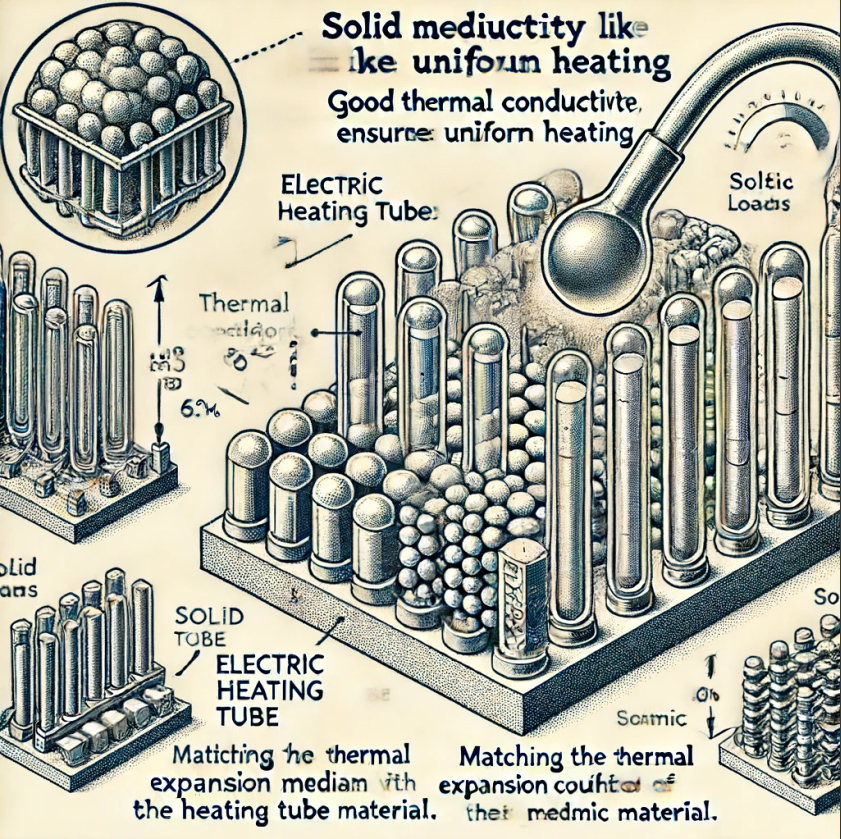
1. Solid Medium: For solid mediums like metals and ceramics, which have good thermal conductivity, heating is usually more uniform. However, attention should be paid to the thermal expansion coefficient of the medium and the compatibility of the electric heating tube material. For solid mediums, electric heating tubes with higher surface loads are commonly used to ensure heating efficiency. The shape and size of the solid medium should also be considered to ensure sufficient contact with the heating tube, enhancing the heating effect.、
2. Liquid Medium: For liquid mediums such as water, oil, and chemical solutions, different flow and thermal properties require different heating tube choices. Immersion-type electric heating tubes are typically chosen for liquid mediums to ensure adequate heat conduction. For volatile or corrosive liquids, corrosion-resistant materials should be used for the heating tubes, and temperature control should be monitored to prevent overheating or evaporation.
3. Gas Medium: For gas mediums like air and nitrogen, the lower density and specific heat capacity of gases usually require higher heating power to achieve the desired temperature. Additionally, the high mobility of gases necessitates that the electric heating tube can effectively operate within the gas flow, avoiding damage due to local overheating. For gas heating, electric heating tubes with rapid response capability and high heat resistance should be selected to ensure precise temperature control.

III. Setting Temperature Control Conditions
After determining the heating object and selecting the appropriate electric heating tube, setting the temperature control conditions is also crucial. Proper temperature control ensures the safety and efficiency of the heating process and extends the lifespan of the electric heating tube.
1. Choosing the Temperature Controller: According to the characteristics of the heating object, select a suitable temperature controller, such as a mechanical thermostat, electronic thermostat, or intelligent temperature control system. The accuracy and response speed of the temperature controller directly affect the temperature control effect.
2. Placement of Temperature Sensors: During the heating process, the installation position and number of temperature sensors should be reasonably arranged according to the size and shape of the heating object to ensure the accuracy and representativeness of temperature measurement. Particularly for large or complex-shaped heating objects, the number of temperature sensors should be increased to achieve more precise temperature control.
3. Setting Safety Measures: In the temperature control conditions, necessary safety protection measures should be set, such as overheat protection, short circuit protection, and leakage protection, to prevent accidents. Additionally, regular inspection and maintenance of the electric heating tubes and temperature control system should be conducted to ensure their normal operation.
In summary, determining the heating conditions for electric heating tubes based on the heating object requires a comprehensive consideration of heating power and the characteristics of the heating medium, along with the proper setting of temperature control conditions. This approach ensures the efficiency, safety, and reliability of the heating process, thereby maximizing the heating effect of the electric heating tubes.