Heating elements are widely used in various industrial and domestic heating devices, such as electric water heaters, electric ovens, and industrial ovens. To ensure the heating efficiency and service life of these devices, it is crucial to reasonably determine the number of heating elements (N value). This article will discuss in detail how to determine the N value of heating elements in a machine.
I. What is the N Value of Heating Elements?
The N value of heating elements refers to the total number of heating elements used in a machine. This number directly affects the uniformity of heating, heating efficiency, and the cost of the device. A reasonable N value can ensure that the device operates in the best condition while avoiding resource waste or uneven heating caused by too many or too few heating elements.
II. Basic Principles for Determining the N Value
The basic principles for determining the N value of heating elements mainly include the following aspects:
1. Power Demand: Determine the total power demand of the device and then determine the required number of heating elements based on the power of a single heating element.
2. Uniform Heating: Ensure the uniformity of the temperature distribution in the heating area to avoid local overheating or underheating.
3. Space Layout: Reasonably arrange the positions of the heating elements according to the internal structure of the device to maximize space utilization.
4. Safety: Consider the safety of the heating elements to avoid safety hazards caused by too many or too few heating elements.

III. Specific Determination Steps
1. Calculate the Total Power Demand:
The total power demand of the device is the first step in determining the N value. The total power demand can be calculated based on parameters such as the target heating temperature, heat loss, and heating time of the device.

2. Select the Power of a Single Heating Element:
Based on the available specifications of heating elements on the market, select the appropriate power for a single heating element. The power range of common heating elements varies from tens of watts to several kilowatts.
3. Determine the N Value of Heating Elements:
Based on the total power demand and the power of a single heating element, determine the required number of heating elements.
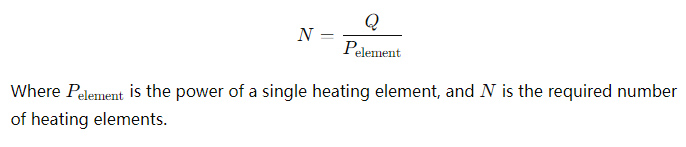
4. Consider Uniform Heating:
After determining the N value, consider the layout of the heating elements in the device to ensure uniform heating. The rationality of the layout can be verified through simulation or experimentation.
5. Evaluate Safety and Cost:
After determining the N value and layout, conduct a safety evaluation to ensure that the working current, voltage, and other parameters of the heating elements are within the safe range. Also, consider cost factors to ensure optimal performance while meeting cost requirements.
IV. Case Analysis
For example, in an electric water heater, suppose we need to heat 100 liters of water from 20°C to 60°C, and the heat loss during the heating process is 1000 watts. The power of the selected heating element is 2000 watts.
1. Calculate the Total Power Demand:
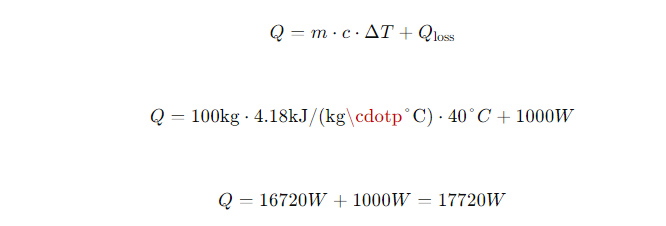
2. Determine the N Value of Heating Elements:
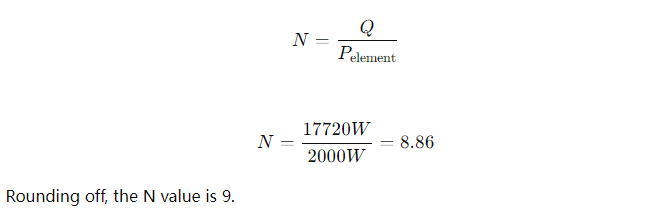
3. Layout and Safety Evaluation:
After determining 9 heating elements, a reasonable layout is needed to ensure uniform heating, along with safety and cost evaluations.
V. Conclusion
Reasonably determining the N value of heating elements is crucial for the performance and safety of the device. By calculating the total power demand, selecting the appropriate power of a single heating element, considering uniform heating, and conducting safety evaluations, the device can be ensured to operate in the best condition. In practical applications, the specific characteristics and actual needs of the device should be considered comprehensively and adjusted accordingly.