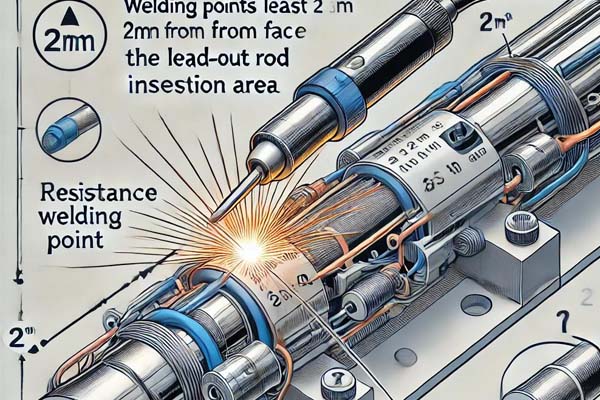
Heating tubes are common heating elements in household electric appliances. Their quality and stability directly affect the product’s lifespan and safety. Ensuring the safety and stability of heating tubes requires excellent manufacturing processes and strict technical standards.
Manufacturing Process Control
Key aspects of heating tube manufacturing include process control, material control, and testing control. Each step influences the subsequent product quality. Self-inspection, patrol inspection, and sampling inspection help maintain quality, enhance pass rates, reduce waste, and ensure product stability.
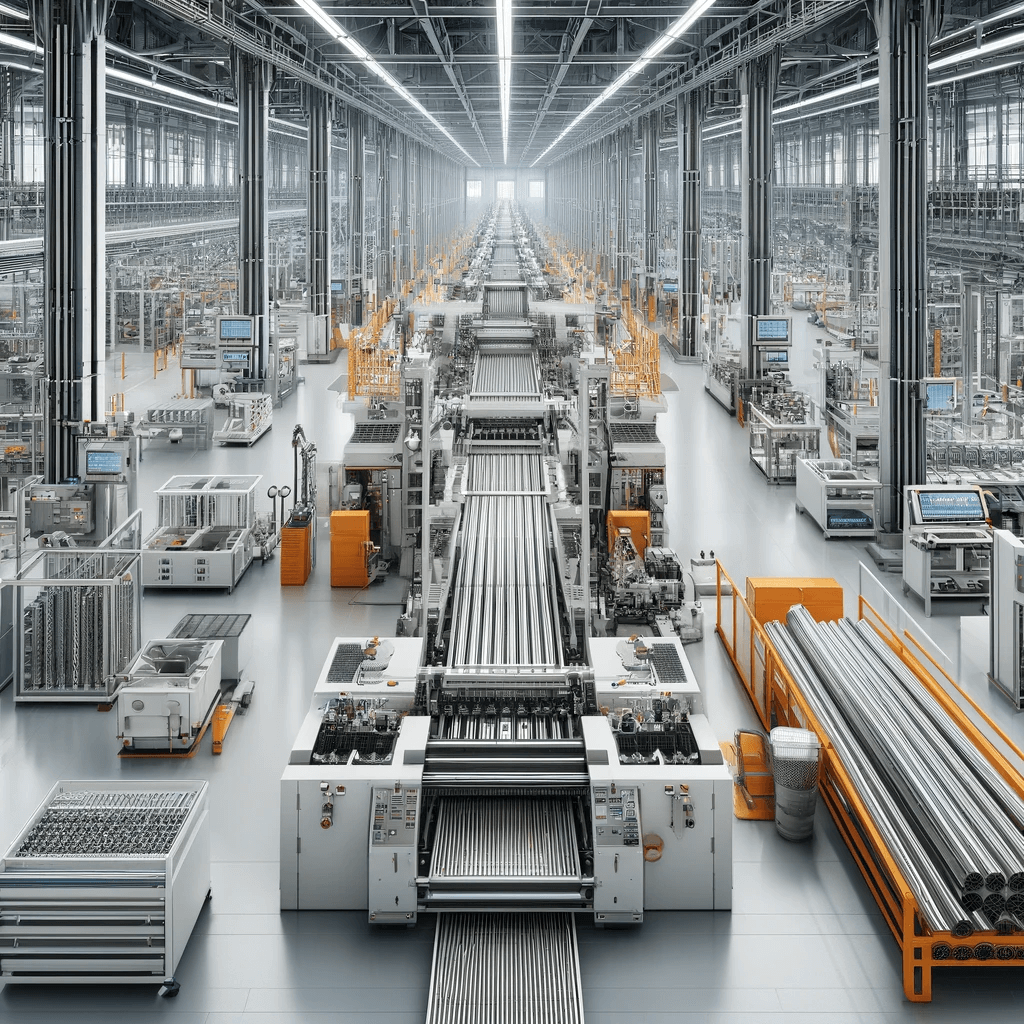
Manufacturing Process Flow
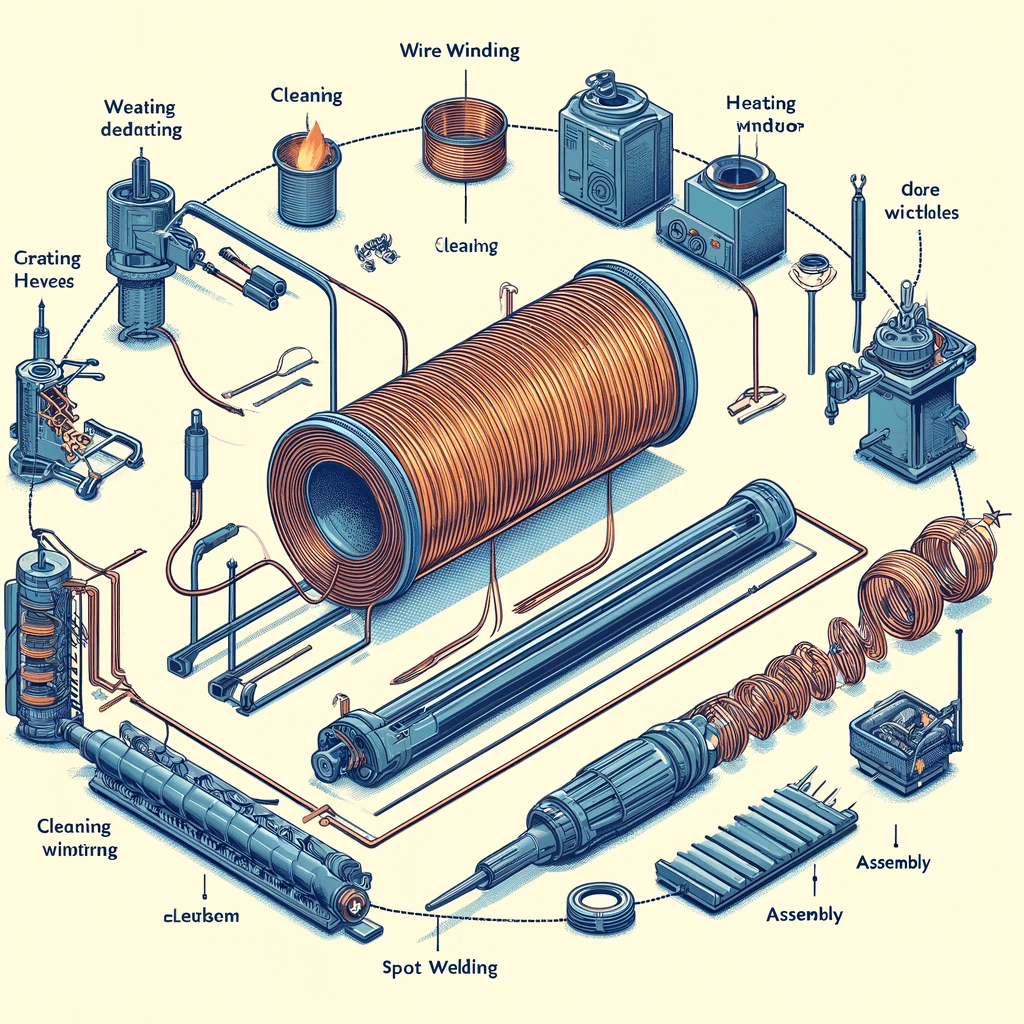
The basic manufacturing process of heating tubes includes: pipe cutting, wire winding, powder filling, pipe reducing, end flattening, heat treatment, bending, sealing, spot welding of sheets or wires, inspection, type testing, and warehousing.
Main Manufacturing Processes
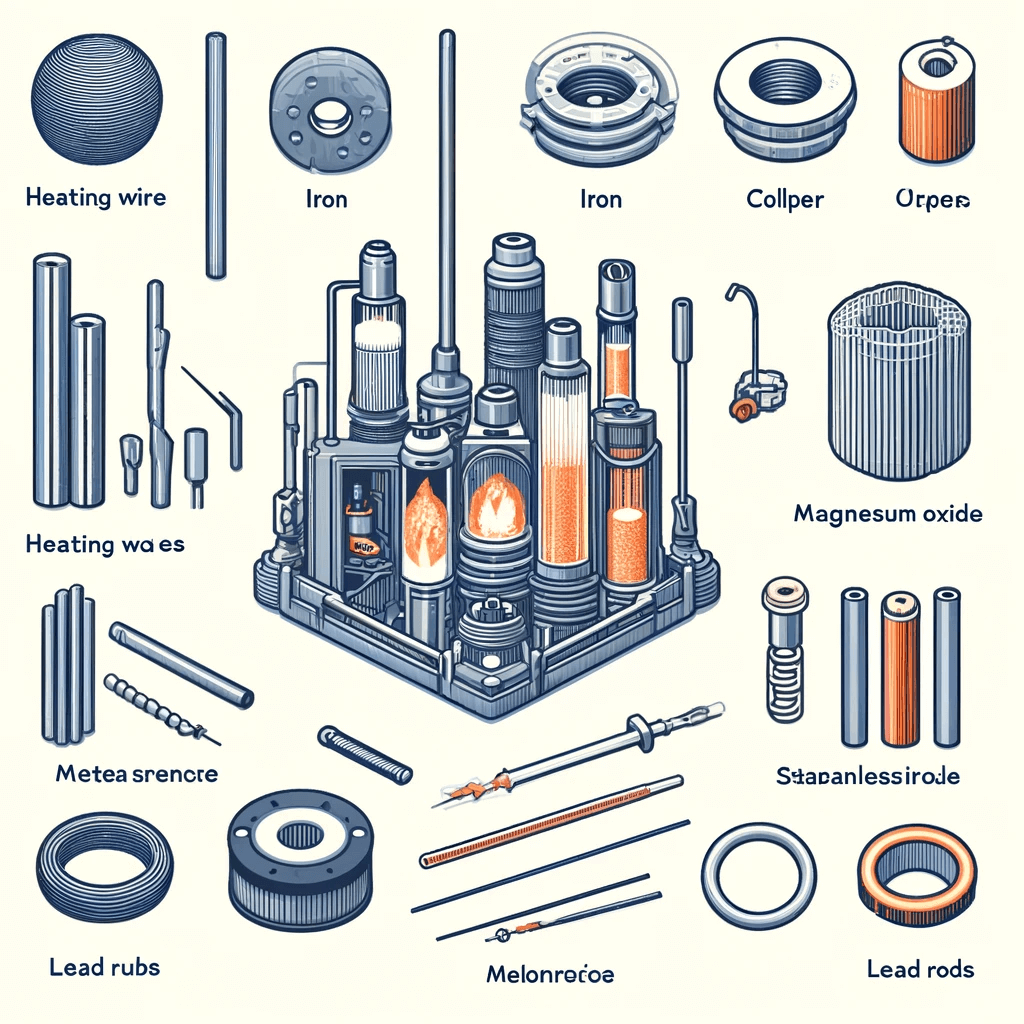
1. Material Components
The primary materials for heating tubes are heating wires, magnesium oxide, tubes, and lead rods. The quality of these materials is crucial. Common heating wire materials include nickel-chromium and iron-chromium-aluminum alloys. Magnesium oxide is a high-purity insulating material with particle sizes controlled within 0.4mm. Tube materials are chosen based on their use, including iron, aluminum, copper, and stainless steel.
2. Heating Wire Winding Process
The winding process of heating wires is critical, involving winding, cleaning, assembly, and spot welding. The external diameter of wound heating wires must be consistent, with even pitch and no overlapping wires. Cleaned heating wires should be free of contaminants to ensure performance.
3. Powder Filling Process
Powder filling is a key process in heating tube manufacturing, directly affecting performance. The filling density should reach ≥2.3g/cm³. Magnesium oxide powder must be stored in dry conditions to avoid contamination.
4. Pipe Reducing Process
Pipe reducing increases the density of heating tubes by reducing the pipe diameter. The compressed magnesium powder density should reach ≥3.05g/cm³. Proper reduction rates are essential for maintaining performance stability.
5. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment softens the hardness of heating tubes for bending and creates a dense protective oxide film on the surface. Methods include mesh belt hydrogen furnace, mesh belt brazing furnace, and high-frequency local annealing.
6. Oil Pressure
Oil pressure ensures the electrical strength of heating tubes, with methods including full-tube and partial-tube oil pressure, and types like D-type, C-type, and oval oil pressure.
7. Moisture Evacuation
Moisture evacuation improves insulation and voltage resistance. Methods include oven evacuation, electric furnace evacuation, and low-voltage evacuation.
8. Sealing
Sealing prevents magnesium oxide from absorbing moisture, ensuring electrical performance. Common sealing materials include RTV silicone, silicone oil, epoxy resin, and glass, chosen based on application, conditions, and cost.
Data Reference
In heating tube manufacturing, controlling magnesium oxide filling density, post-reduction compression density, and heat treatment temperatures is critical for performance. For example, the filling density must reach ≥2.3g/cm³, and the post-reduction compression density must be ≥3.05g/cm³.
FUTAI Heating Tube Production Equipment
Established in 1999, Tongli Machinery (FUTAI) is located in Huiyang District, Huizhou City, Guangdong Province, China. Covering 12,000 square meters with over 6,000 square meters of self-built plant, FUTAI is a large-scale professional factory specializing in automated heating element machinery and intelligent assembly lines. FUTAI integrates R&D, production, marketing, and service, holding independent property rights for most of its machines.
FUTAI supplies a significant number of products to the domestic market while continuously expanding its presence overseas, reaching countries like Turkey, India, Russia, Brazil, the US, Mexico, Japan, and Thailand. FUTAI aims to constantly upgrade and improve product quality, hoping to collaborate with new and regular customers for a bright future.
Conclusion
By implementing rigorous process control, material control, and testing control, heating tube manufacturing can achieve high precision and quality, meeting the modern market’s demands for high-precision heating tube equipment. This enhances product pass rates and lifespan, ensuring safety. With its professional equipment and expertise, FUTAI further ensures efficient and reliable heating tube production, establishing itself as an industry leader.