In the production of electric heating tubes, pipe cutting and material feeding are crucial steps. The quality of these steps directly affects the performance and lifespan of the electric heating tubes, so they must be carried out strictly according to standard process procedures. This article will detail the specific operational requirements and precautions for pipe cutting and material feeding from four aspects: measuring pipe specifications, ensuring the cut is burr-free, controlling the cut width, and maintaining length tolerance.
1. Measuring Pipe Specifications
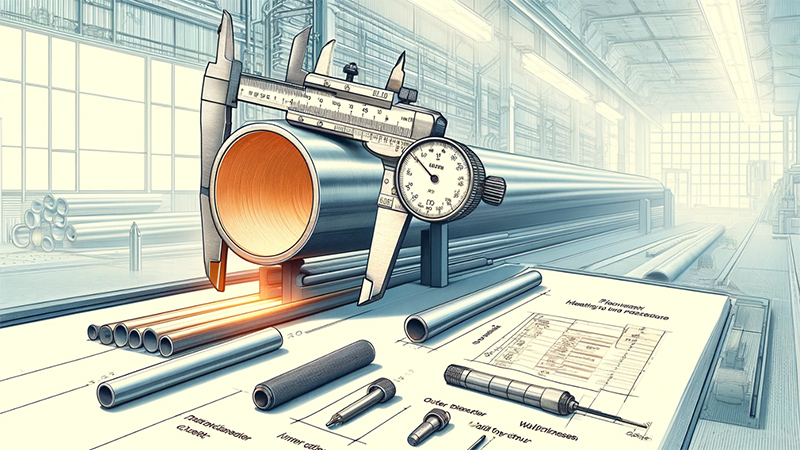
Before pipe cutting and material feeding, the specifications of the pipes to be processed must be accurately measured. This includes parameters such as the outer diameter, inner diameter, and wall thickness of the pipes. Precision measuring tools such as vernier calipers and micrometers should be used to ensure measurement accuracy. The specifications of the pipes directly affect subsequent processing steps and the quality of the final product, so the measurement work must be meticulous and thorough, with no room for error.
2. Ensuring the Cut is Burr-Free
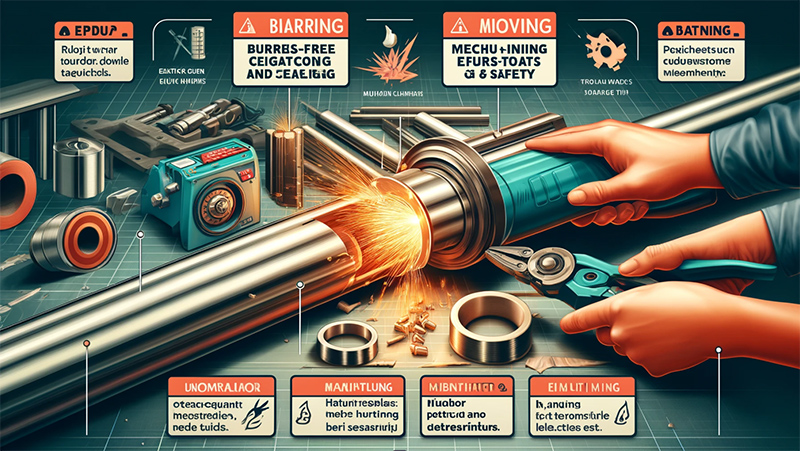
The quality of the cut is a key indicator of the level of craftsmanship in the pipe cutting process. The cut should be free of burrs to ensure the sealing and safety of the electric heating tube. Burrs not only affect the sealing effect of the tube but can also cause injury to operators during installation. To avoid burrs, high-quality cutting equipment should be used, and deburring should be performed after cutting. Common deburring methods include mechanical deburring and manual deburring, with the specific method chosen based on the material of the pipe and the condition of the cut.
3. Controlling the Cut Width
The cut width refers to the width of the cut section of the pipe after cutting. According to standard process procedures, the cut width should not exceed 2.5mm. This requirement is mainly to ensure the tightness and consistency of the electric heating tubes during subsequent processing. If the cut width is too large, it can cause problems during assembly and welding, affecting the performance of the final product. To control the cut width, the cutting tool must be sharp, and the cutting process must maintain a stable speed and pressure. Regular inspection and replacement of cutting tools are also important measures to ensure the cut width meets the standard.
4. Maintaining Length Tolerance
Length tolerance is another critical control parameter in the pipe cutting process. Standard process procedures specify that the length tolerance of the cut pipes should be ±0.5mm. Controlling length tolerance directly affects the installation and performance of the electric heating tubes. If the length exceeds the tolerance range, the tubes may not fit the corresponding components during installation, affecting the normal operation of the entire equipment. To ensure the length tolerance is within the acceptable range, the cutting position should be carefully measured and marked before cutting, and stable operation should be maintained during cutting. Additionally, using high-precision cutting equipment and auxiliary measuring tools is essential for controlling length tolerance.
As a crucial process in the production line of electric heating tubes, pipe cutting and material feeding require meticulous and detailed craftsmanship. From measuring pipe specifications to ensuring the quality of the cut, controlling the cut width, and maintaining length tolerance, each step is critical to the quality and performance of the final product. In practice, strictly following the standard process procedures, using high-quality equipment and tools, and paying attention to every detail are key to successfully completing the pipe cutting and material feeding process. Only in this way can high-quality electric heating tubes be produced to meet customer demands and market standards.