Heating elements are widely used in industrial and household equipment, making their efficiency and durability crucial. However, a common issue with heating elements in practical applications is the formation of scale on their surfaces. The accumulation of scale not only reduces the thermal efficiency of heating elements but also shortens their lifespan. This article explores the simplest methods to reduce scale on the surface of heating elements, aiming to enhance their performance and durability.
I. Causes of Scale Formation
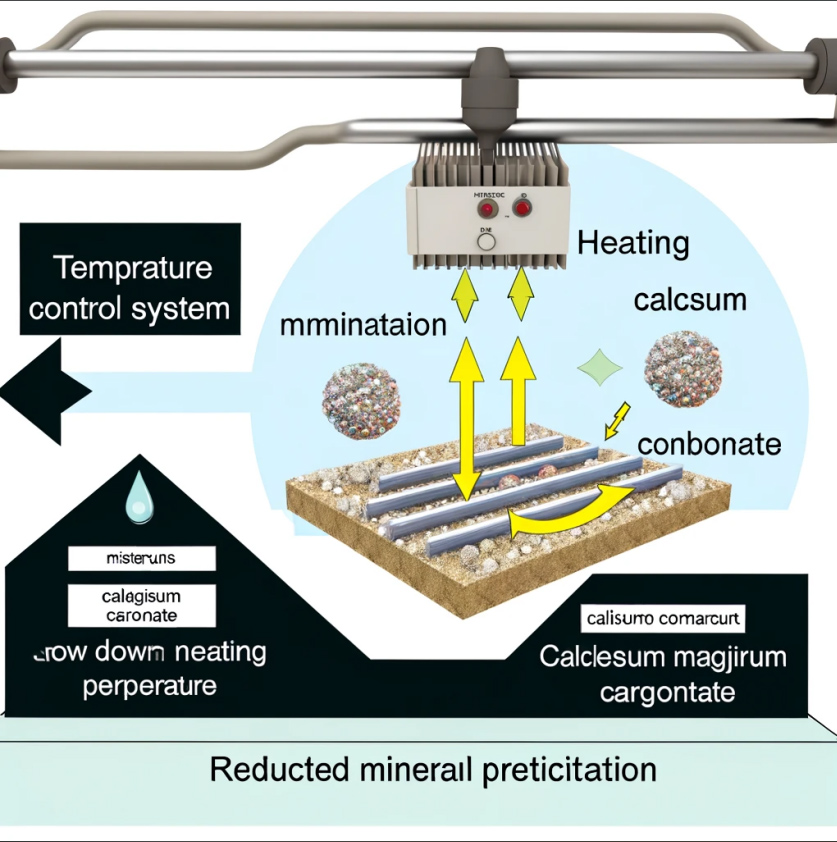
Scale is primarily formed by minerals such as calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate in water, which precipitate at high temperatures. When water is heated by heating elements, these minerals precipitate and adhere to the surface of the elements, gradually forming a hard layer of scale. This not only affects thermal conductivity but also leads to overheating of the heating elements and even causes malfunctions.
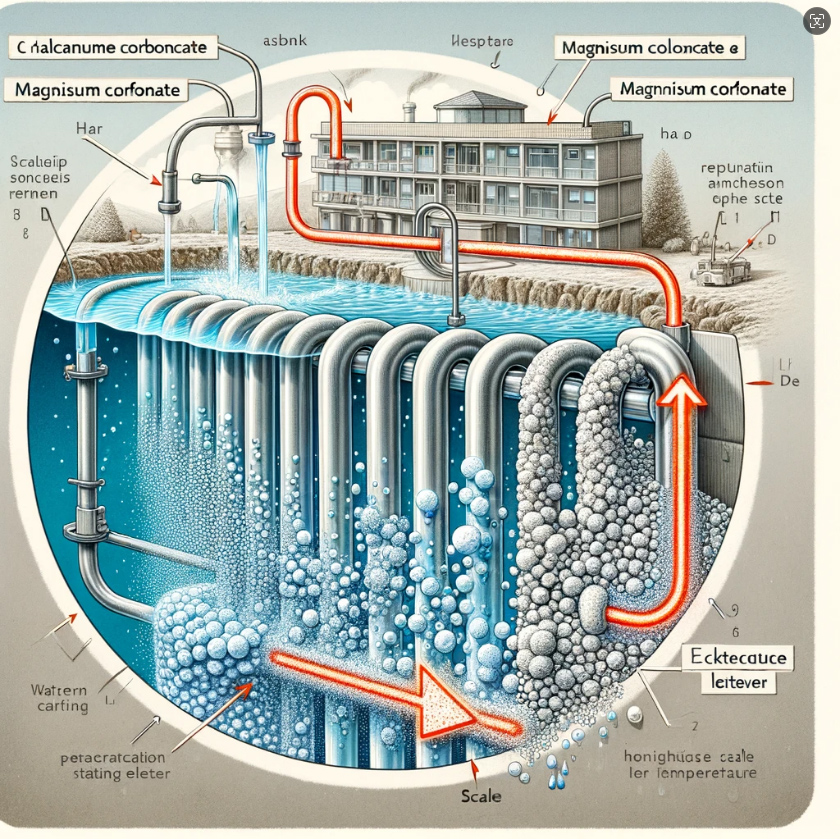
II. Simple Methods to Reduce Scale
1. Water Softening Treatment
The most direct method is to use water softening treatment to reduce the mineral content in the water. Water softening devices can replace calcium and magnesium ions in the water with sodium ions through ion exchange resins, preventing these minerals from depositing on the surface of heating elements. Water softening treatment equipment is easy to operate and suitable for both household and industrial applications.
2. Use of Scale Inhibitors
Adding scale inhibitors to water is also an effective method. Scale inhibitors can suppress the crystallization process of minerals in the water, preventing them from adhering to the surface of heating elements. There are various scale inhibitors available on the market, and users can choose products according to their specific needs. This method is cost-effective, easy to operate, and suitable for various environments.
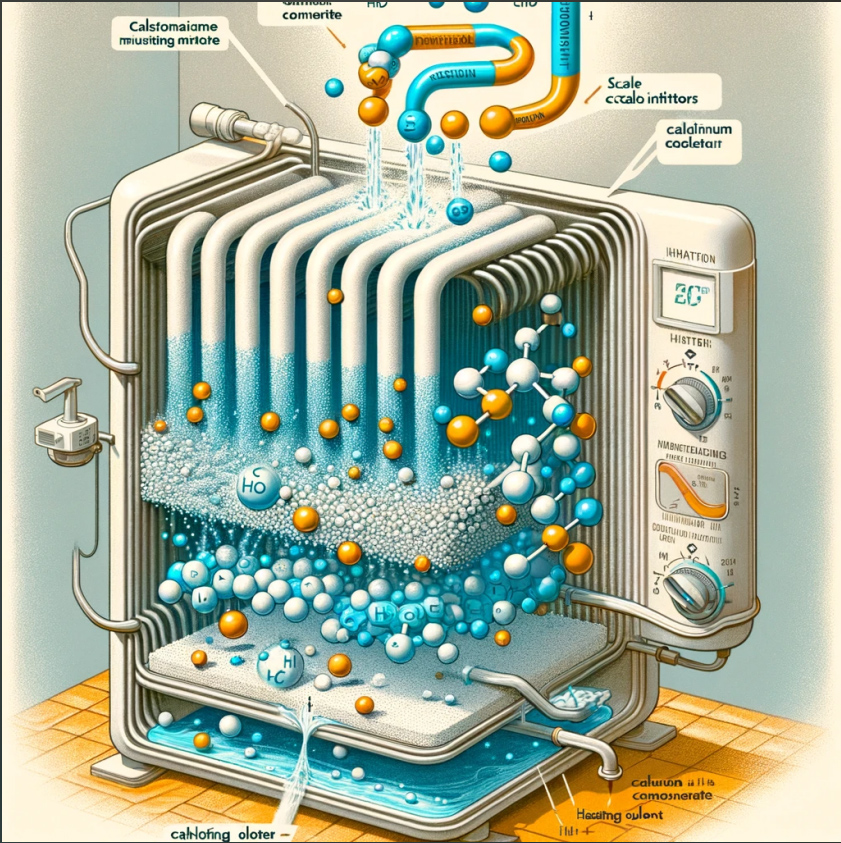
3. Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning of heating elements is an effective means of preventing scale buildup. Both chemical and physical cleaning methods can be used. Chemical cleaning typically involves using acidic solutions to dissolve scale, while physical cleaning involves scrubbing or using high-pressure water jets to remove scale. Regular cleaning not only effectively removes existing scale but also prevents further accumulation.
4. Controlling Heating Temperature
Reducing the heating temperature of the elements can slow down the precipitation of minerals, thus reducing the formation of scale. Properly controlling the heating temperature can extend the lifespan of heating elements and improve heating efficiency. Users can achieve precise temperature control by adjusting the temperature control system of their equipment.
5. Improved Materials and Design
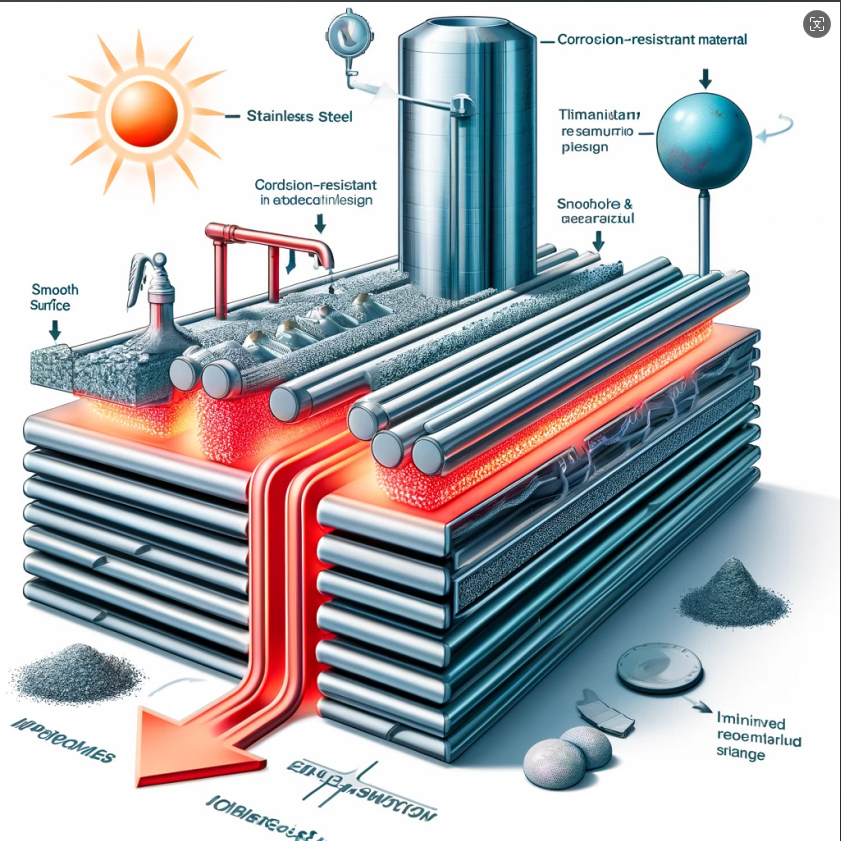
Choosing materials with good anti-scale properties and optimizing the design of heating elements are also important methods for reducing scale formation. For instance, using corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel and titanium alloys can effectively reduce scale adhesion. Additionally, optimizing the surface structure of heating elements to make them smoother and free of dead corners can reduce scale deposition. Although these improvements may be more costly, they can significantly enhance the reliability and durability of the equipment in the long run.
III. Conclusion
Reducing the formation of scale on the surface of heating elements is crucial for enhancing their performance and extending their lifespan. By using water softening treatment, scale inhibitors, regular cleaning, controlling heating temperature, and improving materials and design, the accumulation of scale can be effectively minimized. Users can choose appropriate methods or combine multiple methods based on their specific situations to achieve the best results.
Scale formation is a major challenge in the maintenance of heating elements, but with scientific and reasonable measures, its impact can be minimized. It is hoped that this article will provide useful references for users, helping to ensure the efficient and long-lasting operation of heating elements.